Fogging
Determination of the fogging behavior of materials used in vehicle interiors
FOGGING TEST IN THE
AUTOMOBILE INTERIOR
DAMAGE CAUSED BY SUNLIGHT AND MOISTURE
Weathering tests are the most important material, component and vehicle tests. With imat you can ensure the function and service life of parts, components and vehicles in arid climates (hot and dry climate zone) and tropical climates (warm and humid climate zone). Painted or laminated components, electronic components or entire cockpits are tested in the installation position of a test vehicle. With our two test areas in South Africa, we cover the climate zones similar to Arizona and Florida in the USA.
The focus of outdoor weathering is on chemical and physical signs of ageing. These include changes in color and gloss, delamination effects, deformation, dimensional changes and gaps. In the outdoor weathering of complete vehicles, functional tests during the weathering period are also part of our service in South Africa. The outdoor weathering tests at imat take place in the South African Kalahari Desert, in the KwaZulu-Natal region on the Indian Ocean, on our own test areas. If your requirements call for outdoor weathering in other regions of the world, imat`s engineers will of course also be happy to assist you with the implementation.
In addition to the actual outdoor weathering, our employees also prepare test setups and equip parts, components and vehicles with the necessary sensors. We organize the transport and collection of components and vehicles, including customs clearance to the desired test field.
The Kalahari Desert provides ideal conditions for the long-term weathering of vehicles and materials in a hot and dry climate (classification according to the Köppen-Geiger model).
The maximum temperatures are comparable to those in Arizona, but the fluctuations between day and night and summer and winter are higher.
Upington:
Highest temperature >40°C / Lowest temperature -4°C
Total irradiation 2278 kWh/m²
UV 97 kWh/m²
Sun, salt and humidity accelerate ageing
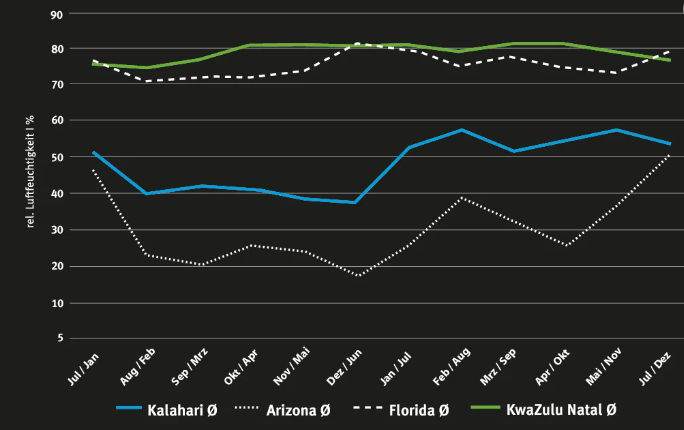
Richards Bay, which is located in the Kwazulu-Natal region on the Indian Ocean, has warm and humid weather conditions. In addition, there is a higher salt content in the air, making Richards Bay comparable to Florida.At our test site, there are opportunities to store vehicles, materials and components in the open air for longer periods of time. Richards Bay has a constantly high humidity of around 75 to 80 percent all year round. The temperature range throughout the year extends from 5°C to 40°C.
Richards Bay:
Highest temperature ~40 °C / Lowest temperature ~5 °C
Total irradiation 1675 kWh/m²
UV 60 kWh/m²
Comparison of the climate data of South Africa with Florida and Arizona
The seasons are offset in South Africa due to its location in the southern hemisphere. Thus, the hottest period is during the northern winter, the coldest months are June and July .
Are you looking for an exam? Standard? Specifications?
Accredited & certified tests
CONTACT OUR EXPERTS
Description. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consetetur sadipscing elitr, sed diam nonumy eirmod tempor invidunt ut labore et
- Tab Title






Frequently asked questions about the fogging test
The sample quantities required for a fogging test depend on the standard and the test method used. Here are the general guidelines:
1. standard DIN 75201 (type A and type B)
-
Type A (glass plate method):
A sample quantity of 10 cm² is typically required. The sample is placed on a heated plate in a sealed chamber and the volatiles released condense on a glass plate above. -
Type B (aluminum foil method):
Similar to type A, a sample volume of approximately 10 cm² is used. However, the volatile substances condense on a cooled aluminum foil.
2. standard ISO 6452 (international standard)
- Sample quantity:
Again, a sample size of about 10 cm² is typically required to evaluate the amount of volatiles released at elevated temperature.
3. other specific requirements
Depending on the specific requirements of the customer or OEM standards, sample quantities may vary. It is important to check the respective standards or test requirements carefully.
Method A - Reflectometric method:
- Principle: This method measures the change in reflectivity on a glass plate on which volatile components from the material sample are deposited.
- Procedure: A material sample is heated in a beaker while a glass plate above it is cooled to 21°C. The temperature difference causes the volatile components to condense on the glass plate. The reflectance index of the fogged glass plate is then measured to determine the amount of condensed material.
- Application: This method is particularly suitable for materials for which an exact determination of the optical fog effect is required.
Method B - Gravimetric method:
- Principle: This method measures the weight of condensed volatiles on an aluminum foil.
- Procedure: The material sample is heated in a beaker while an aluminum foil disc is cooled to 21°C. After 16 hours, the amount of condensed material on the foil is weighed.
- Application: This method is ideal for an accurate quantitative determination of the amount of condensed volatiles.
EMISSIONS & ODOR
Formaldehyd in Fahrzeugen: Herausforderungen für die Automobilindustrie
Read moreStellantis: Freigabe für Emissionsprüfungen erfolgreich (VIAQ)
Read moreVDA 277 vs. VDA 278: Was ist der Unterschied?
Read moreGeruchsunterschiede bei Polypropylen: Die Rolle von Faserverstärkung und Verarbeitungsparametern
Read moreWarum sind die Einheiten der Ergebnisse von Prüfungen der Werkstoffemissionen eigentlich so unterschiedlich?
Read moreGrenzwerte für Formaldehyd und Formaldehydabspaltern in Fahrzeugen
Read moreFREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT TESTS IN DIFFERENT CLIMATE ZONES
We can test and validate the function and service life of parts, components and vehicles in arid climates (hot and dry climate zone) as well as in maritime climates (warm and humid climate zone): painted, laminated or leather-covered test specimens and components, electronic components or entire cockpits in the installation position of a test vehicle. With two test areas in South Africa, we can achieve results comparable to those in Arizona and Florida, USA.